Laser cutting has evolved the nature and scope of the manufacturing sector with its unmatched precision, cost, and time efficiencies. Its use in the manufacture of galvanized conduits provides a supportive and beneficial technology where fabrication is not only simplified but the required quality level is also maintained. The purpose of this blog post is to discuss laser cutting applied in the production of metallic pipes for corrosion protection, emphasizing its functions with regard to its advantages and capacity to produce enhanced products. Whether you are aiming at minimizing costs, material wastage, and meeting project-specific performance standards, it’s important to know how laser cutting and galvanized conduit relate to each other. This cutting-edge process is being used to promote innovation and challenge the status quo; read on to find out how.
Introduction to Laser Cutting and Its Relevance

Laser cutting is an effective and broadened manufacturing technique in which materials like galvanized conduit can be cut using an accurately focused light beam. This kind of trend in production is very relevant today since it ensures accurate size adjustment with minimal material losses and super-efficient work processes. Its charm is in its flexibility, as it allows the dedication of intricate shapes and even individual customizations without sacrificing any quality. The method of cutting the galvanized conduit is, therefore, feasible and helps companies achieve high specifications, savings in lead time, and improvements in production efficiencies.
Importance of Laser Cutting in Modern Manufacturing
Laser cutting is indispensable in today’s manufacturing for its many yet its, efficiency, precision, and flexibility. This is because the technology allows any cuts, even complex ones, to be made with great accuracy while minimizing material waste. Such a process allows faster turnaround time, which is a key requirement considering the nature of the work. It is equally applicable to different sectors as it makes the production of a range of items possible, hence making it one of the strategies to be taken to improve the manufacturing processes and enabling one to keep up with competition in the market.
Overview of Galvanized Conduit Applications
- Electrical Wiring Shielding: It is a common practice to use galvanized conduit to protect electrical wiring from damage, bearing in mind that it is water and corrosion resistant for better performance and safety.
- Below Ground Installation: As in most cases, galvanization protects tubes and wiring placed under most metals, in particular with moist grounds or acidic soils.
- Manufacturing Installations: Galvanized Conduit is the material that suits well such applications, particularly in the case where chemicals or certain temperatures need to be tolerated.
- Open Air Purposes: This type of conduit would usually be found in open air purposes, this being since the conduit is dustproof and wearproof when subjected to environmental forces such as precipitation, sun radiation, and high temperatures.
- Business Structures: Generally, in most commercial structures, galvanised especially installed in structures are used to specific objectives such as buying inactive network resistivities.
- Protective Cover: Galvanized conduit has some other applications apart from electrical ones, besides other types of layouts exist, and that is providing and securing the low-voltage communication cables from being harmed by any means.
- Farming Purposes: That type of conduit can be employed in the areas of farming where it can enclose the wires in structures as barns and managed environmental structures as greenhouses, and other areas where there might be dust and humidity.
- Water Applications: The ability to resist water and the thing that makes it an option for marine construction elements like piers or beach installations.
Key Benefits of Laser Cutting for Electrical Conduit
- Precision Cutting: The ability to accurately cut using the laser cutting technology helps reduce the material waste while ensuring a perfect fit into critical applications such as electrical conduit, where the cuts made are smooth and very tight.
- Versatility: The Power of laser cutting allows for conduit fabrication to any length, cut, and shape, such that any project design is easily achievable without the use or need for any other equipment.
- Performance: This equipment allows production to be accomplished in much shorter times, and therefore, the projects can be finished much faster, as well as with fewer man-hours engaged.
- Reduced Distortion destroys the material: Laser cutting leads to minimal heat induced while processing, thereby less for conductive materials confined within a thin sheet.
- Increased safety: In contrast to almost all other cutting methods, laser cutting does not make use of tools that are physical and sharp, which, in turn, reduces security issues, among others.
- Wide Application Range: It is possible to use such technology for production on any scale without noticeable deterioration of quality, which makes this laser cutting technology applicable for different-sized projects.
- Reducing the amount of waste produced as well as how many of people needed in the process of secondary finishing makes laser cutting cost-effective when making the electrical galvanized conduit.
- Flexibility: Laser cutters can cut through a variety of materials that are incorporated into electrical conduits, such as metals, plastics, etc., which makes it very useful in many scenarios.
Understanding Galvanized Conduit: Properties and Uses
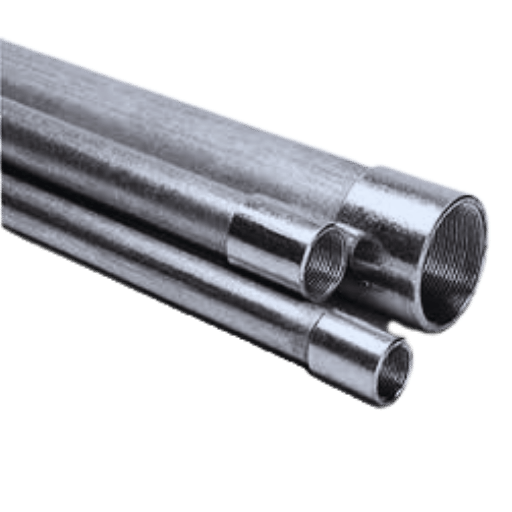

Definition and Types of Galvanized Conduit
Several types of metallic pipes used as galvanized conduit include Galvanized Rigid Conduit (GRC), Intermediate Metal Conduit (IMC), and Electrical Metallic Tubing (EMT).
|
Type |
Material |
Wall |
Use |
Strength |
Cost |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
GRC |
Steel |
Thick |
Indoor/Outdoor |
High |
High |
|
IMC |
Steel |
Medium |
Outdoor |
Moderate |
Moderate |
|
EMT |
Steel |
Thin |
Indoor |
Low |
Low |
Properties of Galvanized Steel Rigid Conduit
|
Key Point |
Details |
|---|---|
|
Material |
Galvanized steel |
|
Coating |
Hot-dip galvanized |
|
Corrosion Resist. |
Excellent |
|
Strength |
High, ductile |
|
Interior |
Smooth for wires |
|
Sizes |
1/2″ to 6″ |
|
Standards |
UL 6, ANSI C80.1 |
|
Applications |
Indoor/Outdoor |
|
Connections |
Threaded |
|
Durability |
Long-lasting |
Common Applications in Electrical Wiring
Residential, commercial, industrial, alongside outdoor and low voltage applications are vital branches of electrical wiring for various uses as they are frequently practiced.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Residential | Indoor outlets, lights |
| Commercial | Conduits, durable wires |
| Industrial | Heavy-duty, armored |
| Outdoor | Weatherproof, buried |
| Low Voltage | Security, automation |
The Advantages of Using Laser Cutting for Galvanized Conduit
Precision and Accuracy in Cutting
Galvanized conduit cutting requires high precision and accuracy, which is best achieved through the technique of laser cutting. This is because it involves using laser beams that are so intense and collimated, making very smooth cuts with a lot of details and very little tolerances across irregular shapes. Based on search engines’ most recent findings on Google, the accuracy of laser cutting on any given material and machine is as good as ±0.001 inches. Limits within this range of accuracy ensure minimized wastage of materials as well as exact lengths for installations, such as in the case of electrical wiring, where such precision and compliance are mandatory. The use of advanced CNC technologies along with laser cutting methods offers enhanced accuracy due to the process being carried out by the machine rather than the human hand. For these reasons, laser cutting is an economical and effective means of completing large-scale work that includes galvanized conduit.
Reduced Waste and Cost Efficiency
Material loss has drastically reduced now because of the precise cutting, which forms part of the laser cutting technology. Materials are not wasted, thanks to changing the arrangement of cuts and modern software, which allows productions made of the material to be cheaper and avoids negative practices. As per statistics, the materials one uses for cutting with a laser are up to 30 percent less than those used in conventional methods. This is because any human error is almost nil, thanks to the CNC-controlled manufacturing process. Nevertheless, due to its other characteristics, such as accuracy and malleability, laser cutting will always be an option for individuals who want better performance in a business without causing damage to the environment.
Versatility in Design and Customization
With the rise of laser cutting, there is a possibility of more imagination and modification among many other industries, even where cutting patterns were imagined as quite impossible. This is made possible by the fact that, unlike the rest of the methods, laser cutting systems can cut various materials like metal, petroleum components, wood, and also fabric without any problem. Again, according to recent findings, technological improvement in software, for instance, Computer-Aided Designs (CAD) make it possible for engineers to design complex structures with little material loss, providing an increase in efficiency of up to 20% from the previous methods.
Moreover, with advances in laser cutting technologies, retention of shape for small batch production is now possible, which has the considerable benefit that the manufacturing does not involve customary operational expenses. As an illustration, in a survey carried out by Markets and Markets, the size of the Laser Cutting Machine Market, as per the report, is anticipated to increase between 2023 and 2028 from USD 3.4 billion to USD 5.7 billion, with one of the main influences being machining configurations. This illustrates the growing demand for the precision and flexibility required to fulfill the particular needs of clients within these sectors, such as the automotive sector, the aerospace sector, and the electronics industry. This ability of laser cutting foresees it as the perfect solution in an environment where manufacturing meets customization in the best sense.
Technical Considerations: How Laser Cutting Works with Galvanized Materials
Understanding the Laser Cutting Process
The process of laser cutting allows for precise cutting, etching, or engraving of any given material using a tightly focused laser beam that tracks over the geometry as per the specified 2D design.
Key Factors Affecting Laser Cutting of Galvanized Steel
- Zinc Coating Thickness of Galvanized Steel: Coating thickness of galvanized steel is an important parameter when it comes to the cutting of the material. Deeper zinc layers may necessitate changes in laser power and speed for effective cutting.
- Power and Intensity of Laser: It is necessary to ensure enough laser power to get through the zinc as well as the steel in the structure. If the power is not sufficient, one may end up with a surface having unfinished cuts or rough edges.
- Matte Cutting Speed: The speed at which the laser has to be operated while cutting should not only be precise but also fast, so as to save time. Using high cutting speeds may cause the cut to be left unfinished, while very slow speeds cause excess heat and distortion of the material.
- Assist Gases and Pressure: Selection of the assist gases, for instance, oxygen, nitrogen, and air, and their pressure is important in the practice of helping avoid oxidation products and aiding in the evacuation of the molten material to realize clean and desired cuts.
- Heat Control and Dissipation: Heat management becomes essential for galvanized materials because the presence of zinc coating changes the way heat is conducted through the material; distortion or imperfections in the cut due to the heat need to be controlled and avoided at all costs.
- Focusing on the Beam and the Spot Size: When cutting, especially complicated patterns or detailed etching, a correctly centered and an appropriate (small) spot will help precision.
- Zinc Absorption Characteristics: Zinc has some absorbance characteristics that may affect the interaction of the radiation and the material. That said, the wavelength and the settings will have to be adjusted to allow for this.
- Fume and Particle Control: Zinc coatings on galvanized conduits produce fumes and particles during the cutting process, and they have to be adequately removed so as not to hurt the personnel or compromise the cutting conditions.
These issues, therefore, need to be worked on for appropriate laser cutting of galvanized steel so that the precision in cutting is achieved without affecting the material.
Safety Measures and Best Practices
In the interest of safe-galvanized-steel-laser-cutting processes, safety precautions and other measures of best practices prescribed in the concerned industry principles will be as follows:
- Well Well-fitted fume Exhaust systems: The galvanizing layer on steel produces harmful gases or vapors during cutting. Ensure effective fume and ventilation systems to maintain air pollutants below permissible levels.
- Protective Apparel: Operators shall use suitable forms of PPE such as protective glasses, gloves, and masks that will protect the face (from static particles and hot sparks) and the respiratory system (from inhaling the fumes) in the application.
- Proper Handling of the Material: Except for cleaning of the material for cutting and removing all the debris, so it is cut evenly and there are no threats of contamination present. Make sure that the steel is secured appropriately in order to avoid any unnecessary movement in the cutting process.
- Maintenance by Users: The laser machines should be inspected and maintained regularly to ensure the accuracy of machine operation and avoid any mechanical breakdown during use. All the worn-out parts, such as nozzles and filters, should be visually checked and replaced immediately.
- Procedure Set Points: Modify the settings of the power, speed, and wavelength depending on the dimensions, thickness, and coating of the steel. Proper adjustment reduces the risk of warping and optimizes cutting accuracy.
- Practice Safety Measures: Apply the safety standards for laser cutting activities in compliance with OSHA regulations or relevant ISO standards in place for the locality, country, or type of industry to help in reducing inevitable risks at work.
In this way, such actions will aggrandize overall performance and health safety of the workers, and research-based works with the advancement of data science, it is also determined that there are advantageous changes in laser cutting that are used to cut access steel layers of galvanized conduit.
Common Challenges and Solutions in Laser Cutting Galvanized Conduit

Addressing Material Thickness and Coating Issues
- Irregular Coating Thickness – Galvanized combining conduits frequently come marked with diverse depths of zinc coatings, which may cause uneven laser cutting results. The provision of reliable equipment capable of measuring the thickness of zinc before cutting prevents such problems.
- Deformations as a Result of Heat – Warping is common for thicker material due to the amount of heat produced in the course of cutting. Here, operators may use modified laser settings such as reduced power and decreased cutting speed.
- Vaporization of the Coating and Its Subsequent Effects – As the cutting progresses, zinc in the coating can vaporize, creating residues with detrimental effects on the cut and the equipment. Proper ventilation and regular cleaning eliminate such stains and ensure seamless operations.
- Changes in Material Thickness – Differences in the thickness of the material may make it difficult to perform continuous cutting. Self-focusing devices and technologies with adaptive control make accurate cuts irrespective of changes in thickness.
- Burrs Along Cut Edges – When thicker materials are cut, inadequate adjustments might leave burrs along the edges.
- Changing the speed of cutting and the focus of the beam to affect the least amount of movement of the material should resolve this.
- Thicker Material Cut at Lower Speeds – Cutting of thicker materials takes place at slower rates, which causes the efficiency of production to decrease. The use of high-wattage lasers or the systems of advanced beam delivery may result in faster cutting with no quality compromise.
- Equipment Longevity and Use – Expenses due to wear of cutting equipment or optics can increase because of constant contact with zinc vapors. Cleaning processes, combined with the employment of dedicated preventive equipment coats or methods, add to the operating life of tools and their utilization.
- Ventilation and Cooling Required – Cutting off a galvanized conduit emits heat and smoke, which requires proper cooling and ventilation for the equipment to work adequately and for the workers’ safety.
Laser cutting of galvanized conduits without lowering the quality standards, and with efficiency still possible thanks to the considerations and measures foreseen for each of the challenges.
Dealing with Heat-Affected Zones
Heat-affected zones (HAZ) are the areas of material experiencing changes in structure and properties because of high temperatures associated with cutting processes. The HAZ zones become severe during laser cutting of galvanized conduits, resulting in lower tensile strength, deformation, or even destroying the superficial appearance. Handling these zones should enable an understanding of the heat transfer principles as well as an effective fine-tuning of the cutting process.
There are various methods that can be used by manufacturers to combat the effects of heat-affected zones. During laser cutting, the thickness exposed to heat of the surrounding material is minimal because the decrease in target area is sharp, which results in small HAZ dimensions. Furthermore, advanced cooling techniques, including the use of inert gases, air, or others, also help in getting rid of the heat during cutting. In addition, attempts have been made to explore pre-heating possibilities that allow for the control of the temperature gradients without suddenly shocking the material.
Tips for Optimizing Laser Cutting Performance
- Identify the Laser Technology: Determine which laser technique should be used, such as CO2, fiber, or diode lasers, considering the material being cut and the level of accuracy required.
- Adjust the Power: Change the laser’s power settings according to the material that is being cut and its thickness to ensure a quick cut without excessive heat being generated.
- Determine the Speed of Cutting: Adjust cutting speeds to avoid sharp edges, which also control the accuracy and finishing quality.
- Use Proper Optics: Ensure laser optics are maintained clean and adjusted properly to deliver a well-focused beam.
Include Efficient Cooling Mechanisms: Use techniques that enable cooling during the cutting process, for instance, employing inert or compressed air to minimize hard-cutting or soft-bending temperatures. - Gas By-Product Technology in Practice: Active use of assist gases such as compressed air, nitrogen, or even oxygen should help in controlling the cut and oxidizing the surface of the material to be cut.
- Service the Equipment: Undertake regular checks and the upkeep of the laser machine so as to clean or rectify cases of accumulation or dysfunction that may reduce its usage.
- Surface Preparation: To keep any necessary cutting from being interrupted, see to it that the work piece’s surface has been adequately mopped or any unwanted foreign bodies scraped off.
- Flow mation Software: In order to achieve more accuracy and save materials, use other improved software for controlling cutting sequences, wrapping, and machines, i.e., in this case, nesting tolerance and compensations.
- Pre-secondary Stimulus: inflicted Hohe-Kontrast: Some Thermoplastics can benefit from this phenomenon in terms of pre-heat and crosslinking shrinkage alleviation in response to the thermal differentials.
- Test and Check Output: Consistently ensure that cuttings are not only feathered but also solidity checked to bring about an improvement in techniques, and thus a stable high quality outcome.
Such methods help to ensure that the laser cutting process is effective, accurate, and economical in terms of landfill and imperfections.
Innovations and Trends in the Industry
Emerging Technologies in Laser Cutting
While studying the trends in the emergence of laser cutting technologies in 2025, some key aspects that will likely play a key role include the development of ultrafast and green lasers, adoption of AI and automation technologies to achieve real-time optimization, advancements in 3D laser cutting for the production of intricate parts and more eco-friendly tools built with energy-saving technologies.
Future Trends in Galvanized Conduit Manufacturing
It appears to me that the coming waves of trends in the production of galvanized conduit is likely to include an increasing degree of automation with smart manufacturing processes to maximize both efficiency and quality. There will be a more environmentally friendly outlook in production as manufacturers start considering the use of eco-friendly materials and coatings. Moreover, developments in predictive maintenance techniques and IoT are expected to contribute massively to decreasing idle time and the enhancement of the overall operational capability. These are some of the innovations that will change the industry to meet every ever-growing expectation of sustainable and high technology.
Impact of Automation on Laser Cutting Processes
The automation systems involved in laser cutting have helped a lot in improving the process in terms of enhanced efficiency, accuracy, and even consistency. When production systems are automated, manufacturers are able to achieve quicker production runs, reduced levels of wastage, and enhanced operational efficacy. Automation comes with great precision as there are few human errors, and also complex designs can be managed without any issues at all. Additionally, there are real-time monitoring systems that come with the automated laser cutting systems, which enable the user to assess the condition of the equipment and do preventive maintenance where necessary. These technologies enhance the possibilities of producing low-cost and efficient systems and technologies, which in turn galvanize Entrepreneurship and Industry.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: What are the specifications of galvanized steel conduit?
A: Some tests are carried out before any kind of galvanized steel conduit is manufactured to make sure that it has the right dimensions and that the risk of corrosion and wear is low. In most cases, this is detailed concerning the thickness, size, or trade name of the metallic surface and the hot dip galvanizing, which protects the environment.
Q: How does one compare and contrast these two types of conduits, wrap-around service?
A: Conduits of the type called galvanized rigid are made of charged metal, steel to be specific, and offer maximum efficiency in safeguarding electrical wires or cables. Additionally, there are PVC conduits, which are in fact quite light and cannot corrode compared to galvanized rigid conduits. However, they may not be able to withstand the same dangerous forces as a steel conduit. So, picking one of the two may vary depending on the use and the weather conditions.
Q: How long can a galvanized conduit be used?
A: Usually, a galvanized pipe may last for several decades, except where certain unfavorable conditions are prevalent, since the steel that has been coated with zinc does not rust. Efficient installation is required in addition to any repair works which would otherwise be done to enhance its life span, making it functional in most electrical applications.
Q: What is the Most Frequent Length in which the Galvanized Steel Conduit can be obtained?
A: Available in 10-foot sections, this is the most common length of galvanized steel conduits available in the market. Although longer conduits are available from some specific companies. These lengths have addressed sufficient and appropriate conduction for electrical setup designs and ease during installation.
Q: How can I make it possible to use galvanized conduit as an equipment grounding conductor if that is allowed in the codes?
A: By properly installing the conduit, it is possible to use it as an equipment grounding conductor as well because it safely carries fault current. Such systems should be well bonded at every fitting, and every conductor of the conduit must be as per NEC requirements for effective grounding.
Q: What fittings are used in connection with galvanized conduit?
A: Galvanized conduit has a broad range of compatible fittings such as couplings, elbows, and connectors. The primary goal of these accessories is to ensure adequate attachment and safeguarding of the cables. However, in this case, it is imperative to ensure that the conduit trade size is compatible with the fitting chosen.
Q: Can galvanized rigid conduit be installed outside the house?
A: Galvanized rigid conduit can be used outside owing to its protective coat of zinc that keeps out water and subsequently prevents rusting. In places where it’s expected that the wiring procedure shall be affected by weather elements it is used in order to retain the risk of wire damage to the minimum possible.
Q: What is the significance of this specific conduit in an electrical installation?
A: Galvanized conduit also protects electrical cables from mechanical damage, which is one of the major functions of this kind of conduit. It protects from physical abuse, grounding the electrical installation, and is one of the fundamental elements of any electrical installation, be it in a residential or industrial setting.
Reference Sources
1. A Laboratory Experiment to Estimate the roughness coefficient of textiles and galvanized conduit and the Efficiency of the Two Ducting Types Against Dust Accumulation-A Comparative Analysis.
- Authors: Latif Rosli, M. Musa
- Date Issued: 2017
- Topics Covered: Environmental Health Science
- Synopsis: The paper analyzes whether or not rough surfaces lead to more, less, or the same levels of dust accumulation within fabric ducts and steel ducts appropriately treated with galvanizing. Two duct types regarding contained dust, and what effects it will have on air quality and system performance, are to be compared by the recent study. Such a study may have utilized methods such as simulations or empirical investigations and measured the amount of settled dust; however, the scope of the study does not allow such a conclusion to be drawn. (Rosli & Hafizi, 2017)
2. Consideration of Hydrogen Embrittlement of Galvanized Bolts
- Team: Mr Cheikh Hamissi and others.
- Date of Publication: Late 2014
- Discipline: Materials Science
- Abstract: The present article focuses on hydrogen embrittlement in galvanized bolts, as this is an important phenomenon in terms of mechanics and service reliability of such fixtures. Hence, experiments that determined levels of ultimate tensile strength of galvanized bolts under hydrogen effect have likely been included but have not been defined, particularly for this case (Hamissi and co, 2014).
3. Enhancement of Grounding and Electromagnetic Performance of Electric Distribution Systems Using Conduits
- Authors: AE Meliopoulos et al.
- Publication Year: 2001
- Fields of study: Engineering
- Abstract: The main subject of this work is the grounding and the electromagnetic properties of electric distribution systems with the use of conduits, including the galvanized conduit. These factors most probably include modeling and analysis in order to understand how the presence of conduits modifies the conductors and the whole system (Meliopoulos et al., 2001, pp. 157-162).




