Across various sectors, carbon steel plates are instrumental due to their unparalleled strength and adaptability in use. There is hardly an engineering or infrastructure developed that does not rely on construction, manufacturing, automotive, energy, and countless other sectors. What exactly makes carbon steel plates so essential? And how do you determine what type best suits your requirements? In this article, we go into detail on carbon steel plates, their composition, classifications, properties of interest, and applications. Whether novice or experienced, this guide arms you with vital industry knowledge to maximize the efficiency and effectiveness of carbon steel plates.
What is a Carbon Steel Plate?

A carbon steel plate is a sheet of steel that mainly comprises iron and carbon. Its components define its strength and value in various industries, as it is highly durable and versatile. The carbon content in the carbon steel plates ranges from 0.05 to 2.0%, which impacts the hardness and tensile strength of the plates. Due to the high value in construction, manufacturing, and other branches of engineering, carbon steel plates have become greatly popular because of their favorable characteristics to endure stress and pressure, making them suitable for structures, machines, and heavy equipment parts.
Defining Carbon Steel and Its Properties
Carbon steel is an alloy based on iron that consists of carbon in the range of 0.05% to 2.1%. It is distinguished by its strength, malleability, weldability, as well as heat treatment ability.
How Steel Plates Differ from Other Metal Sheets
The differences between steel sheets and steel plates are in their thickness, strength, metal sheets’ durability, and application. In comparison to sheets, plates are thicker and stronger, intended for heavy-duty applications, whereas flexible sheets are used for lightweight applications.
| Parameter | Steel Plate | Steel Sheet |
|---|---|---|
|
Thickness |
>6mm |
0.5-6mm |
|
Strength |
High |
Moderate |
|
Durability |
High |
Moderate |
|
Flexibility |
Low |
High |
|
Applications |
Heavy-duty |
Lightweight |
|
Processing |
Hot-rolled |
Cold-rolled |
|
Uses |
Construction, machinery |
Automotive, appliances |
|
Cost |
Higher |
Lower |
The Role of Carbon Content in Steel
The properties of steel are greatly influenced by carbon content. Although higher carbon concentrations typically increase hardness and strength, ductility is reduced, and the material becomes less malleable. Low-carbon steel, which has less than 0.3% carbon, is soft, more ductile, and weldable, which makes it useful in automotive and construction parts. With 0.3-0.6% carbon, Medium-carbon steel possesses adequate ductility and tensile strength, which makes it useful for tools and machinery. With over 0.6% carbon, high-carbon steel becomes extremely strong and wear-resistant, which makes it suitable for use in cutting tools and springs. The exact steel carbon content determines its appropriateness for certain uses, as strength, durability, and workability are weighed.
Exploring the Types of Carbon Steel Plates
Characteristics of Low-Carbon Steel Plates
| Key Point | Description |
|---|---|
|
Carbon Content |
0.05%-0.3% |
|
Ductility |
High |
|
Malleability |
Excellent |
|
Weldability |
Superior |
|
Strength |
Moderate |
|
Corrosion Resistance. |
Limited |
|
Thermal Conduct. |
Moderate |
|
Density |
2.85-8.08 g/cm³ |
|
Melting Point |
1420-1460°C |
|
Applications |
Construction, Auto, Pipes |
|
Advantages |
Affordable, Versatile |
|
Disadvantages |
Low strength, Rust |
Understanding Medium Carbon Steel and Its Uses
The medium-carbon steel is used in the manufacture of gears, crank shafts, axles, certain parts of machinery, and railway tracks because of having 0.30%-0.60% carbon content. It strikes a nice balance between strength and ductility.
The Advantages of High-Carbon Steel Plates
- High Strength and Hardness: Striking ‘high strength’ and ‘hardness’, high-carbon steel plates withstand exceptionally well, seeking materials requiring endurance, high power.
- Wear Resistance: Abrasive, high wear resistance against abrasion of these plates makes them appropriate for heavy-duty equipment and tools.
- Edge Retention: Sharp edge maintenance has also proven especially useful for cutting tools and blades over longer periods.
- Heat Treatment Capabilities: Further treatment of high carbon steel plates can be done heat-wise to achieve added features like enhanced hardness and improved toughness.
- Versatility in Applications: High-strength wires and springs, as well as industrial machinery, keep tools and dies mounted up.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Outperformed by other alternatives, high-performance materials, high carbon steel plates exhibit specialized properties whilst retaining affordability.
What are the Uses of Carbon Steel Plates?
Common Structural Applications for Carbon Steel
| Category | Applications | Key Features |
|---|---|---|
|
Construction |
Frames, pipes |
Durable, ductile |
|
Automotive |
Gears, axles |
Strong, lightweight |
|
Machinery |
Tools, springs |
Abrasion-resistant |
|
Tools |
Cutting tools |
Hard, sharp edge |
|
Cookware |
Pans, knives |
Non-reactive, durable |
|
Manufacturing |
Fasteners, coils |
Wear-resistant |
|
Appliances |
Washers, clips |
Cost-effective |
Why A36 Steel Plate is Popular in Construction
The versatility, strength, and cost-effectiveness of A36 steel plate make it an indispensable material in the construction industry. It is a low-carbon steel with excellent weldability, aiding fabrication of complex structures. The material demonstrates a good balance of toughness and ductility, which helps in enduring prevalent stress in building frameworks and bridges. Adaptability enables ease of cutting, shaping, and machining into different parts, simplifying workflows in construction.
Trends and recent information suggest that searches for “A36 steel plate applications” and “construction grade steel plates” have been on the rise. Increased searches for A36 steel plate applications suggest people are becoming more aware of its use in infrastructure projects. Part of this demand stems from the plate being available in different thicknesses and sizes, providing flexibility to engineers for designing load-bearing structures. In addition, it is relatively expensive compared to high-performance alloys or alternative construction materials, making it a useful option for low-budget projects while maintaining quality. Thus, A36 steel plate is a staple in modern construction due to its unmatched performance and economic advantages.
The Role of Carbon Steel in Fabrication and Manufacturing
Carbon steel is widely used in manufacturing and fabrication due to its strength, versatility, and adaptability. Recently, I came across industry trends and search data, and I noticed the most frequently asked question was “Why is carbon steel such a favored material in almost all industries?”. The explanation revolves around the optimal mechanical properties and cost-efficiency offered by this steel. Due to its ease of bending, welding, and machining, carbon steel is used in the fabrication of pipelines, machinery, automotive parts, and structural frameworks.
Furthermore, the evolving heat treatment processes increase the hardness and durability of the material, thus increasing its usefulness in harsh conditions. Its recyclability also supports sustainable manufacturing, which is increasingly sought after by numerous industries. Carbon steel stands unmatched when it comes to affordable production and strength, customization options, and fulfilling worldwide manufacturing requirements efficiently and dependably.
How Does Hot-Rolled Steel Differ from Cold-Rolled?

Understanding the Hot Rolled Process
The procedure of hot rolling includes heating the steel slabs to the required temperature for recrystallization, removing scale, and rolling to obtain the desired thickness, followed by coiling, thus producing steel products for diverse sectors.
The Benefits of Cold-Rolled Steel Plates
- Enhanced Strength and Hardness: Cold-rolled steel evolves through processing at or above ambient temperature, leading to enhanced tensile strength and hardness relative to hot-rolled steel.
- Improved Surface Finish: Visually critical applications can employ these plates due to their smooth, polished surface, thereby minimizing the need for supplementary finishing processes.
- Cold Rolling results in tighter tolerances and precise dimensional accuracy, producing homogeneous, uniform products suitable for precision engineering. This is why cold rolling is preferred.
- Better Mechanical Properties: Increased ductility and formability allow cold-rolled steel plates to endure demanding fabrication processes.
- Refined Surface: Improved treatment of the steel results in a smoother coating and uniform composition, which provides a better foundation for protective layers, thereby counteracting corrosion more effectively if treated correctly, improving anti-corrosive properties.
- Cold-rolled steel frozen in versatility marks adaptability within industries such as automotive, construction, aerospace, and appliance manufacturing due to the quality enhancements across sectors.
Comparing Thickness and Surface Finish
Evaluating thickness and surface finish involves comparing roughness, machining productivity, wear resistance of coatings, as well as specific measurement methods.
| Parameter | Thickness | Surface Finish |
|---|---|---|
|
Definition |
Layer depth |
Peaks & valleys |
|
Measurement |
Micrometers |
Ra, Rz, Rt |
|
Techniques |
XRR, AFM |
Profilometry, AFM |
|
Durability |
Varies |
Affects adhesion |
|
Cost |
Material-based |
Process-dependent |
|
Applications |
Coatings |
PCB, metals |
|
Standards |
ISO, ASTM |
DIN, ISO |
What are the Grades of Carbon Steel Plates?

Exploring Different Grades of Steel
Steel is categorized into four main grades: Carbon, Alloy, Stainless, and Tool steels.
| Grade | Key Elements | Properties | Uses |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Carbon |
Iron, Carbon |
Strong, Ductile |
Construction, Tools |
|
Alloy |
Nickel, Chromium |
Corrosion Resistant, Durable |
Machinery, Automotive |
|
Stainless |
Chromium, Nickel |
High Corrosion Resistance |
Medical, Food Equipment |
|
Tool |
Tungsten, Vanadium |
Heat Resistant, Hard |
Cutting, Drilling |
How Alloying Elements Affect Steel Properties
Alloying elements improve the strength, hardness, Corrosion resistance, toughness, and wear resistance of steels.
The Importance of Manganese in Steel Grades
Steel’s characteristics are significantly augmented with the addition of manganese. As I understand it, manganese enhances the strength, toughness, and wear resistance of steel, especially for demanding applications. It also serves as a deoxidizer during steelmaking, aiding in the removal of impurities. Moreover, manganese increases hardenability, enabling the steel to attain desired mechanical properties via heat treatment. In the absence of manganese, steel would be more susceptible to becoming brittle and prone to cracking, which in turn, diminishes its versatility and dependability.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: What are the different types of carbon steel plates?
A: Carbon steel plates comprise three categories, which are low carbon steel plate, high carbon steel plate, and medium carbon steel plate. The varying types of steel differ in their carbon content and mechanical properties, which makes them suitable for different applications.
Q: What is the difference between low-carbon steel and high-carbon steel?
A: Low carbon steel, or mild steel as it is commonly referred to, is softer and more ductile due to its lower carbon content. This increase in ductility makes it easier to machine and weld. High carbon steel’s higher carbon content increases its hardness and strength but decreases its weldability.
Q: How do the mechanical properties of carbon steel plates affect their applications?
A: The mechanical properties, such as yield strength, toughness, and ductility, are critical for determining the applications of carbon steel plates. A good example is for structural steel, where high strength is important, and for forming processes, good ductility is important.
Q: What are the common applications for carbon steel plates?
A: Carbon steel plates are widely used in various fields such as construction, storage tanks, automotive, shipbuilding, and the manufacturing of machinery. The specific type of steel plate is selected according to the required mechanical properties and environmental conditions.
Q: In what ways does a high-carbon steel plate differ from an alloy steel plate?
A: The main difference is the composition of both plates. High carbon steel plate consists of carbon and iron with a high percentage of carbon, which increases the strength and hardness of the steel. On the contrary, alloy steel plate contains alloying elements like chromium or nickel, which are added to improve desired characteristics of the steel, for example, its corrosion resistance or toughness.
Q: What are the Benefits of Using Rolled Steel Plates?
A: There is an ease in procuring and bending hot rolled plates because steel sheets are hot rolled, unlike cold rolled steel, which comes at a premium and requires slabs of steel to be heated to high temperatures first. This is because hot rolled steel undergoes requisite inflation in temperature to ease the process of manufacturing it into thinner plates and strips.
Q: What does Carbon Steel Sheets Galvanizing Entail?
A: The means of extending the existence of steel sheets is done by layering a shell of zinc over them, which protects them from decaying. More particularly, galvanizing sheets of carbon steel is very important as it increases the longevity of carbon steel sheets, more so in moist conditions or where chemicals are involved.
Q: What Should You Consider When Choosing Your Carbon Steel Plate Supplier?
A: Aside from the established reputation of the supplier, there are carbon strip plate grades the supplier has at hand, if they can offer custom cuts as well as the various other quality assurance certifications the supplier has, their turnaround delivery times, and post-delivery customer service provided. Meeting the needs of your order must be enforced to ensure that not much is left to work.
Q: In what aspects does cold-rolled steel differ from hot-rolled steel in its applications?
A: Due to being processed at room temperature, cold-rolled steel has a smoother surface and more precise dimensions than hot-rolled steel. It is used for applications needing tighter tolerances and a better surface finish, while hot-rolled steel is used in areas where such details do not matter as much.
Reference Sources
1. Corrosion behaviour of hot-rolled composite steel plate of 316L stainless steel and A6 carbon steel for marine applications
- The authors: Ye-ke Liu et al.
- Published in: Journal of Materials Research and Technology
- Publication date: July 1, 2023
- Citation: (Ye-Liu et al., 2023)
Key findings:
- The work centers on the composite steel plates of 316L stainless steel and A6 carbon steel from the corrosion behavior science perspective within seawater conditions.
- It emphasizes selection criteria and the behavior of the materials for marine engineering infrastructures, specifically focusing on corrosive environments.
Methodology:
- The authors performed corrosion tests on the composite steel plate to assess its performance in corrosion rate and microstructure.
2. The Mechanical and Metallurgical Properties of Joints Resulting From Rotary Friction-Welding of Low Carbon Steel Plates and Rods
- Authors: Dhamotharakannan Thirumalaikkannan et al.
- Published In: Key Engineering Materials
- Date Of Publication: 28 November 2022
- Citation:( Dhamotharakannan et al., 2022, pp. 153–160)
Research Highlights:
- This study examines the rotary friction welded joints between low carbon steel plates and rods concerning their mechanical and microstructural features.
- It was revealed that the tensile strength of the welded joints was better than that of the base materials, demonstrating the joint geometry enhancement with welding.
How The Research Was Done:
- The research included weld quality evaluation through tensile testing, along with microstructural examinations via Scanning Electron Microscopy SEM.
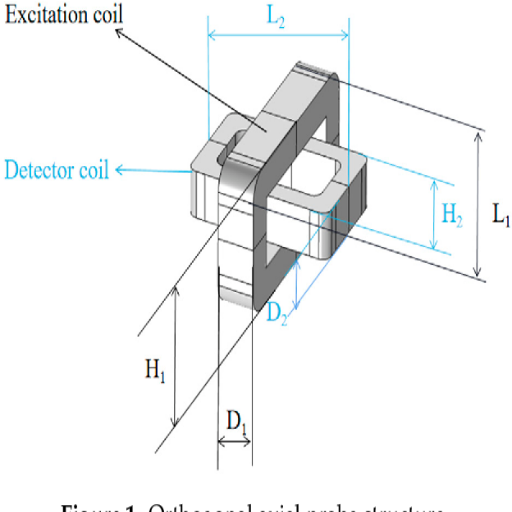
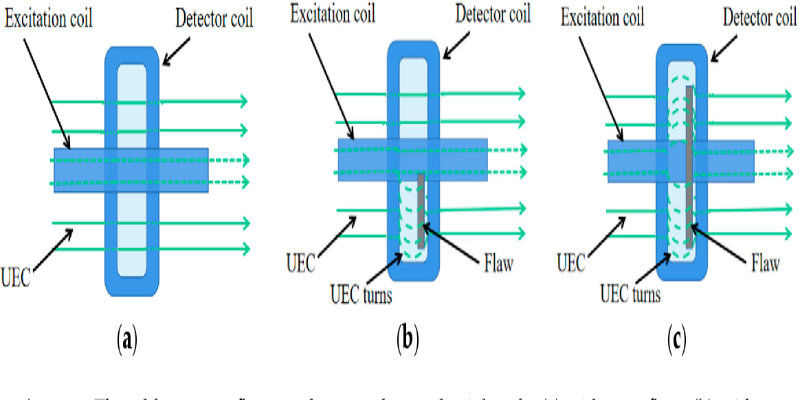
3. Research on Detection Mechanism of Weld Defects of Carbon Steel Plate Based on Orthogonal Axial Eddy Current Probe
- Authors: Linnan Huang et al.
- Published in: Sensors (Basel, Switzerland)
- Publication Date: September 26, 2020
- Citation: (Huang et al., 2020)
Key Findings:
- This article proposes a novel detection mechanism for weld defects on carbon steel plates employing an orthogonal axial eddy current probe.
- The research shows that the probe considerably overcomes the lift-off effect due to unevenly welded surfaces, thus detection accuracy is enhanced.
Methodology:
- The authors described a finite element simulation model to study the probe’s performance and tested it systematically for detection using carbon steel specimens.
4. Carbon Steel Microstructure – U.S. Naval Academy: This document explains the microstructure of carbon steel, which illustrates its properties as well as its plate-like structures.
5. Federal Register – Certain Cut-To-Length Carbon-Quality Steel Plate: This publication registers government documents containing policy and commerce information concerning carbon-quality steel plates.
6. Carbon steel




