Integral parts for different types of industrial uses are provided by the Steel pipe fittings. A zealous example is the normal position of the oil and gas pipelines and alterations in the chemical and power fields. In a number of available standardizations, there is one ASTM A234 standard that is a mark of quality and trust. In this paper, everything associated with ASTM-A234-steel-pipe-fittings, such as features, uses, and advantages, will be discussed in detail. A better way to understand why ASTM A234 is considered the gold standard in all these many fields, whether you are a professional engineer, a manager, or simply an enthusiast wishing to learn more about such technology, the following article will be very useful. Feel great and participate with us in deconstructing these fittings while explaining how they make critical operations efficient, long-lasting, and comply with other things.
Introduction to ASTM A234
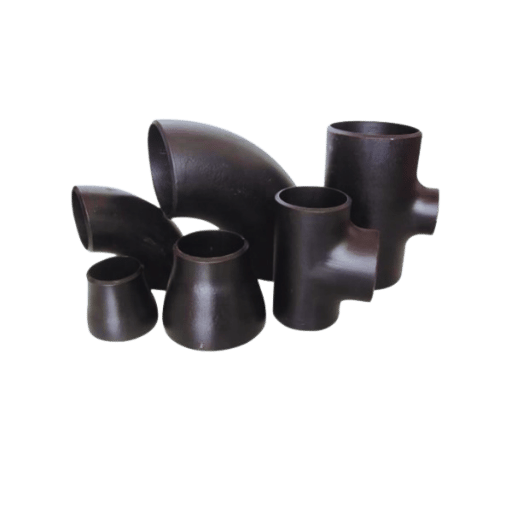

The specification, in accordance with the ASTM A234 standard, covers pipe fittings made of wrought carbon steel and wrought alloy steel, which are used in pressure piping services when the temperature of the piping is high. These types of fittings are made for seamless and welded pipes and are used more broadly to join, resurface, or end sections of pipes. The standard enables equipment to work smoothly and safely even under adverse conditions and is often used in oil and gas, power, as well as other processes. The main advantages of the ASTM-A234 steel-pipe fittings are their high mechanical properties and excellent resistance against corrosion. Most importantly, they are made with very tight tolerances to ensure safe use and operations.
What is ASTM A234?
The American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM) released the ASTM A234 standard, which defines the production requirements for fittings made out of wrought carbon steel and alloy steel used for low to high-temperature piping installations. These include various types of fittings used to make modifications to or open sections of pipes in oil and gas, chemical processing, or power industries, as the most common examples. The content of the specification limits itself to higher quality standards of the fittings regarding the materials, Sciana complexity, and the service requisites so that their workings are not disruptive even in all-in shooting situations.
Importance of ASTM Standards in Pipe Fittings
ASTM standards are sufficiently important to help maintain the quality, safety, and performance of pipe fittings for different purposes. The standards set rules for the composition of the material, production, and testing for the fittings to be used in different operationally demanding conditions. Manufacturers who observe ASTM standards provide parts that have the same characteristics, work as expected, and fit easily with other parts of the system, thus minimizing failures that come with such equipment and regulations of the industry. This helps to promote safety and efficiency so that compliance with the ASTM standards is inevitable, especially for the design or maintenance of a piping system.
Overview of Carbon and Alloy Steel Pipe Fittings
Components for connecting, steering, and changing the direction of pipelines are necessary in most of the key industries dealing with carbon and alloy steel pipe fittings, of course. Carbon steel pipe fittings have qualities such as strength, resistance, and cheapness; hence, they are good for use in high-temperature and high-pressure applications. On the other hand, other alloys that have chromium, molybdenum, or nickel tend to be more corrosion-resistant, heat-resistant, and wear-resistant. Such fittings can be found in places where some extreme conditions prevail; for instance, in the chemical industry, power plants, or oil and gas sectors. Choosing one or the other is a matter of operational need, such as fluid type, temperature, pressure, and others.
Types of ASTM A234 Steel Pipe Fittings

A234 WPB Carbon Steel Pipe Fittings
The construction of A234 WPB carbon steel pipe fittings is made to withstand medium to high temperatures. Their main function is to create elbows, reducers, berk tees, and caps in gas and water piping systems. All astm-a234-steel-pipe-fittings come with ASTM standards and can be used for pressure pipes and welding joints, among others. Due to their sturdy nature, they are commonly used in various industries such as power, refining, and petrochemical.
A234 WP11 Alloy Steel Pipe Fittings
A234 WP11 alloy steel pipes and fittings are made to withstand both high temperature and pressure. They are highly durable and are also resistant to heat and corrosion, thus finding applications in industries like power plants, the petrochemical industry, and oil and gas, among several others. They adhere to ASTM-A234-steel-pipe-fittings, thereby guaranteeing performance and protection in all adverse working conditions. The most common designs are elbows, tees, reducers, and caps, thereby allowing application to all varying piping system needs.
Comparison of A234 Fittings with Alternative Materials
Comparative evaluations are characterized in relation to materials, including ASTM A234 steel pipe fittings, with alternative materials such as stainless steel, nickel alloys, chrome moly steels, and based on the properties of strength, temperature resistance, corrosion resistance, and cost.
|
Parameter |
A234 Fittings |
Stainless Steel |
Nickel Alloys |
Chrome-Moly Steel |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Strength |
High |
Moderate |
Very High |
High |
|
Temp. Resist. |
Moderate |
High |
Very High |
Very High |
|
Corrosion |
Moderate |
High |
Very High |
Moderate |
|
Cost |
Low |
High |
Very High |
Moderate |
|
Usage |
General |
Corrosive |
Extreme |
High Temp |
Mechanical and Chemical Properties of ASTM A234 Fittings

Mechanical Properties of ASTM A234 WPB
- Tensile Strength: The minimum tensile strength of astm-a234-steel-pipe-fittings is 485 Mpa that is 70,000 psi. Hence, it guarantees high strain load resistance.
- Yield Strength: These units possess the capacity of 240 Mpa, also known as 35,000 psi, making it possible for deformations without losing any function.
- Elongation: The transition period of these fittings usually ranges between 20 and 30% elongation, indicating that they entail a considerable degree of deformability.
- Hardness: ASTM-A234 WPB fittings possess a hardness level not exceeding 197HBW(Brinell scale). Such a level is considered suitable because it is neither too hard nor too soft to impede machining.
- Impact resistance: These fittings are highly impact resistant, especially at room temperature and thus can be used in heavy duty industrial processes.
Chemical Composition of A234 Carbon and Alloy Steel
Enhanced steel components, such as ASTM A234 fittings, maintain a precise design owing to the chemical composition of the alloy. The elements in the alloy result in mechanical properties and performance at the required levels. Several specific elements are discussed briefly as follows:
- Carbon (C): 0.30% or less.
- Manganese (Mn): 0.29-1.06.
- Phosphorus (P): 0.05% or less.
- Sulfur (S): 0.05% or less.
- Silicon (Si): 0.10% Minimum.
- Chromium (Cr): 0.40% Maximum for alloy steel category.
- Molybdenum (Mo): 0.15% Maximum for alloy steel category.
- Vanadium (V): 0.08% Maximum.
- Nickel (Ni): 0.40% Maximum.
- Copper (Cu): 0.40% Maximum.
These help to meet all quality requirements and enable the use of ASTM A234 pipe fittings in demanding industrial situations.
Benefits of Using ASTM A234 Steel Fittings
- Exceptional Stiffness and Durability: ASTM A234 makes fittings for high-pressure and high-temperature applications, thus confirming that they are suitable for rigid industrial processes.
- Resistance to Corrosion: The alloy offers superior protection from rust, allowing it to deliver for extended periods in adverse conditions.
- Wide Range of Uses: They are easy to employ in many sectors, such as the petrochemical, power, and oil and gas sectors.
- Fabrication with Relative Ease: Welding and manufacturing of the ASTM A234 fittings into different configurations and sizes can be efficiently done enhancing the piping design and the installation processes.
- Observance of Norms: Developed in adherence to the ASTM norms, such pipe fittings assure a high degree of uniformity in the end products, and do not leave any scope for compromise on standards set by the industry.
Manufacturing Process of ASTM A234 Pipe Fittings
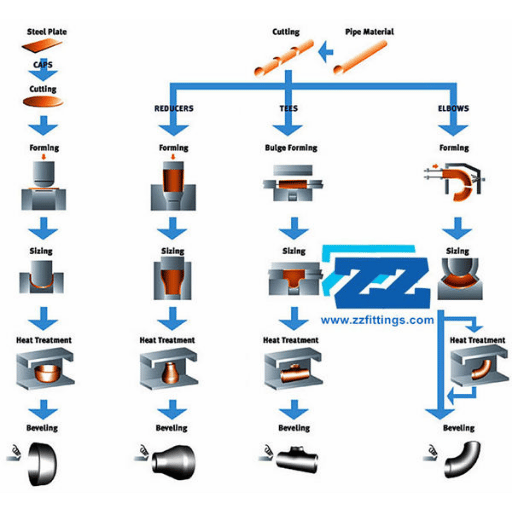
Manufacturing Techniques for Steel Pipe Fittings
Steel pipe fitting materials and components are fabricated to be strong, accurate, and compliant with relevant standards and regulations by using specific processes. Below are some of the most widely used methods:
- Forging- in order to forge steel pipe fittings, high temperature is needed to heat the billets or bars, and then hit with a hammer or press in order shape the fitting. Hence, this helps to obtain better configuration of the structure of the fitting.
- Buttwelding- when it is impossible to bend the pipe into the desired shape, it is called buttweld pipes that are heated and then bent on the sides so that fitting can be done.
- Machining – this is where the steel is manufactured into the necessary fittings through the use of desired instruments and devices that are able to reach delicate detail and edges.
- Heat Treatment: As soon as the form of the fitting is achieved concern, attention is put on improving its properties such as strength, risk of stretching and resistance to rust or rusting.
Quality Control in ASTM A234 Production
Quality management in the production of ASTM-A234-steel-pipe-fittings consists of the following steps that have to be taken in order to make sure the fitting is produced according to the regulations and uses as follows:
- Material Control – First of all, it is necessary to inspect the chemical and mechanical properties of raw materials in order to make sure that they are effectual to the ASTM requirements.
- Dimensional Study – This involves taking measurements of the fitting that has been manufactured to ensure that it meets the size and the tolerance requirement.
- NDT or Non-Destructive Evaluation – Methods such as ultrasonic or X-ray radiography are considered as ways of assessing fitment normal and defect level fitment without operating or subjecting the fitments to surveillance working tests.
- Pressure Proving – This involves compressing or stressing the fittings in order to test if it can resist the applied pressures.
- Surface Stainless-Steel Control – It includes the surface inspection of each piece to look out for any cracks, keep any rust and any deformation at bay.
It follows that the final product of this technology is always safe in use, dependable, and able to perform its specific functions.
Ensuring Durability and Performance Standards
For applications where longevity and efficiency are critical, the construction of industrial fittings is pegged on meeting three fundamentals that include:
- Quality Control – This demands that one selects materials of very good quality to improve their toughness and defense against wearing out, rusting or harsh environment.
- Testing Procedures – Deficiency or already failed components are addressed by extensive testing like assessing threats from pressure and observing surfaces of welds.
- Meeting the Required Specifications—Fulfilling all the technical expectations regarding different aspects of the product and the accompanying certificate.
This is how producers assure the users of getting application specific components that are robust and retain functionality for long durations.
Applications of ASTM A234 Steel Pipe Fittings

Industrial Applications of A234 WPB Fittings
- Oil and Gas Industry – Within this sector, they are principally made use of in pipeline systems for transporting crude oil and natural gas and other petroleum products due to their high strength and durability.
- Chemical Processing Plants – Necessary for heating systems for treating many fluids, pressure elements, and corrosive chemicals, amongst other major chemical processing handling formations.
- Power Generation – This is used in thermal and nuclear plants for thermal and nuclear power generation piping of high temperature and high pressure networks connections aspects.
- Petrochemical Industry – Used in many refining processes and the transport of petrochemical products.
- Water Treatment Facilities – Applied in water transport and treatment systems, including some desalination plants, and also industrial wastewater treatment facilities.
Commercial Uses of ASTM A234 Steel Pipe Fittings
- Construction & Infrastructure – Facilitating structures of buildings, bridges, infrastructures on larger scales, in particular highlighted by their rugged and robust features.
- HVAC – A component of any heating or cooling system that provides ventilation to the proper region of the house.
- Agricultural – A basis for irrigation systems directed towards watering crops within the farmlands or cultivated regions without any setbacks.
- Chemical processing installations – Important for moving chemicals which are under a lot of pressure and heat, providing Online looking in most cases.
- Hydrocarbon Distribution – Invaluable for transporting systems’ transformation of different crude oils, gases, and their derivatives without collapse or deformation in a strenuous working environment.
Case Studies on Successful Projects Using A234 Fittings
Natural Gas Pipeline on the Continent
- Gaps such as A234 fittings were used in the infrastructure within which natural gas was transferred out of a cross-border pipeline. These fittings performed exceptionally well under high pressure and temperature casualties enabling disruption-free delivery of gas that is spread across cultivable areas.
Petrochemical Facility in the Middle East
- A234 fittings were widely used in the course of a refinery facility expansion amidst high temperatures whose functions were to ferry chemically exhaustive materials. So important were their strongly built and rust free characteristics to the plant’s efficacy and its long term sustainability.
Water Plant on the Continent
- A234 fittings have been used in the water supplies and pressure control systems of a very successful hydroelectric power plant project. These fittings sustained high water flow rates and pressure changes, ensuring that the plant constantly achieved its objectives without any distractions.
Compliance and Standards for ASTM A234

Understanding ASTM A234 Compliance
ASTM A234 is a standard that specifies requirements for the production of fittings intended for pressure piping systems and elevated temperature service. The standard regulates aspects such as the chemical and precision mechanical properties and manufacture of the materials, assuring that their use will not be limited to certain conditions. One of the aspects of compliance relates to the class of the material used, the application of heat treatment processes, and the provision of the correct dimensions. All these requirements assure the production of standard ASTM-A234-steel-pipe-fittings in order to function optimally in harsh conditions.
ANSI B16.9 Standards and Their Relevance
ANSI B16.9 outlines the criteria for factory-welded wrought butt-weld fittings that are made to specific dimensions, tolerances, and performance requirements. Consequently, the intended purposes of these fittings are achieved due to the quality of the products, the design of their spigot and socket, and the operational loads anticipated. In addition, ANSI B16.9 promotes uniformity, reliability, and convenience of facilities that use piping systems in industries for different purposes without jeopardizing the safety and reliability of operations.
The Role of Standards in Ensuring Safety and Performance
Standards are necessary in regulating the design and manufacture of components to the desired state for safety and performance. They create universal standards that ensure quality, failure prevention, and system compatibility. ANSI B16.9, for instance, helps a lot by not only lowering the risks associated with the industry processes, enhancing operational efficiency, but also by enabling the industries to adhere to the set standards, guiding the regulatory bodies. This consistency aids the achievement of safety, reliability, and interoperable frameworks across most of the applications.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: What are the applications of ASTM A234 piping fittings?
A: ASTM A234 steel pipe fittings are devices installed in piping systems to alter or connect piping lines. These are fabricated from carbon and alloy steels in accordance with ASTM A234 for the purpose of fitting pipelines. These fittings are usually required in the oil and gas, chemical, and power industries, because such fittings offer thermal and pressure resistance.
Q: What kinds of piping fittings can be accommodated in accordance with ASTM A234?
A: ASTM A234 is concerned with a range of piping fittings, such as elbows, T pieces, reducers, end caps, bends, and lap joint stub ends. They are made to enable other pipes, include crossings, changes in sizes and closes ends. All of these thus have a definite functional role in ensuring that the piping system is constructed accurately and functionally.
Q: What are the essential aspects of materials used in manufacturing ASTM A234 fittings?
A: ASTM A234 fittings are particularly renowned for their mechanical properties, such as excellent tensile strength, impact strength, and abrasion resistance. They are applicable for holding fluids at high temperatures and pressures. The properties of the products result from the kinds of carbon and alloy steels contained in ASTM A234, since they ensure the material’s good performance in hostile conditions.
Q: Do ASTM A234 pipe fittings come in different grades?
A: Yes, ASTM A234 fittings are divided into different grades such as WPB, WPC, WP5 based on materials applied and heat treatment applied in the process of their development. For instance, WPB fittings are fabricated using carbon steel and hence, can only be used in typical services, while WP5 fittings are made using alloys and are used for high temperature services.
Q: Are there any heat treatment processes that need to be performed on ASTM A234 fittings?
A: Depending on their composition and the usage, ASTM A234 fittings are usually subjected to specific heat treatment processes like annealing, normalization, or tempering. The structure of these fittings is improved due to the treatments done which guarantee that they will bear the stress in the form of pressure, temperature, and many others which might be caused during the handling of the fitting.
Q: What is the process followed in the preparation of ASTM-A234-steel-pipe-fittings?
A: The Process of manufacturing the above-mentioned fittings is to forge, Form, and Weld, and then carry out heat treatment. With forging, the manufacturers can form the fittings out of metal billets, which offer high strength and integrity. Some of the forming operations that are available include bend and press, and these enable manufacturers to meet the desired shapes, among others, while welding assemblies of the straight sections of the pipe in particular arrangements.
Q: What is the distinction between ASTM A234 seamless pipe fittings and ASTM A234 welded pipe fittings?
A: Seamless pipe fittings such as ASTM A234 have no inserted joints; the entire fitting is made from a single piece of steel. Such seamless pipe fittings are useful when leakages are not permitted. Pipe fittings for low-pressure and standard leakage control can, however, be produced by welding sections of steel together. While seamless fittings can be applied in extreme environments, welded fittings are affordable and can be used in most noncritical applications.
Q: What are the specifications of ASTM A234 fittings?
A: The dimensions of pipe fittings produced to the ASTM A234 standard are often determined by many standards, for example, ASME B16.9 and MSS SP-75. These standards guide the dimensions of fittings and their tolerances, as well as the verification procedures to be followed in different fittings.
Q: What measures do you take in preparation for the ASTM A234 manufacturing program to ensure quality is controlled?
A: This control measure, in the case of ASTM A234, is what appears in all applications as the most intensive test protocol with sound reasons characterized by particularly extensive checking, checking for leakages, and so on. The internal imperfections are sometimes measured only in the condition of such fittings with the use of non-destructive methods, such as ultrasound or X-ray. Industrial standards application allows the fittings to be consistent and effective, and satisfies the safety requirements.
Q: Can ASTM A234 Fittings work in corrosive atmospheric conditions?
A: While ASTM A234 pipe fittings have immense strength and durability, corrosion resistance levels vary depending on the fitting’s grade and finish. For example, carbon steels should be coated with additional protective coatings such as paint or galvanization to prevent corrosion in aggressive environments. Chromium-containing alloy steel grades are more corrosion resistant.
Reference Sources
- Hydronic Piping in Buildings
Texas A&M University Facilities Design Standards
The ASTM-A234-steel-pipe-fittings standard is discussed in the hydronic piping systems for buildings. - Design Standard – Hydronic Piping for Utility Plants
Texas A&M University Facilities Design Standards
This pamphlet provides information on the ASTM A234/A234M types of fittings and execution. - Hydronic Piping Standards
Florida Institute of Technology Facilities Standards
There are moderate and high temperature conditions, so construction materials such as ASTM A234 fittings are considered. - Steel
- Alloy steel
- Carbon steel




