In the construction and industrial markets, black steel pipes have always been respected for their qualities, particularly strength, durability, and cost-effectiveness. But the familiar question is, does black steel pipe rust? Some professionals and homeowners alike entertain this question. A little knowledge will go a long way to understanding how to maintain this material and use it accordingly in projects. We will look into what black steel pipe is, when it corrodes, and most importantly, the best ways to prevent rust from damaging its life. By then, you will know all that is required about how to maintain and preserve black steel pipe to get maximum performance in your applications.
Introduction to Black Steel Pipes
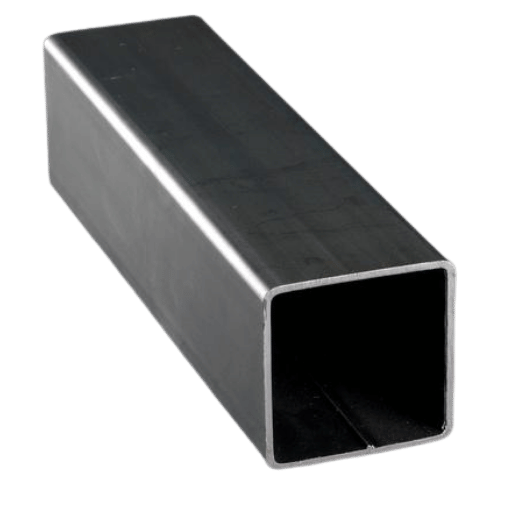
Black steel pipes come in various shapes, suitable for applications where rust resistance or pressure from a high-temperature environment is not a concern. Their black surface thus characterizes them without any protective coating, such as paint or galvanization. Mechanical strength is the most crucial consideration for black steel pipes, and their durability and cheapness enhance their use in the transmission of gases, water, and non-corrosive substances. Their black surface, not being coated, will easily produce rust when exposed to moisture, so they should be protected in environments with high humidity.
What is Black Steel Pipe?
Black steel pipe is a kind of steel piping that is not coated and is mainly used to convey gas and water in low-pressure and low-corrosive environments. Known as black steel pipes due to the dark iron oxide scale formed on their surface during manufacturing, these pipes are preferred for their strength and low cost. They are generally used in industries, construction, and mechanical systems where corrosion resistance is not an issue.
Composition of Black Steel
The main elements that constitute black steel and give it strength and durability are carbon and iron. Carbon in black steel pipes may range from 0.05% to 0.25%; therefore, it is always going to be low- or medium-carbon steel. The reason for this is that the material is sufficiently rigid for general applications at an affordable price. Trace amounts of some other elements such as manganese (up to 1.65%), sulfur (0.05%), and phosphorus (0.04%) may also be present. These might get there during the steelmaking process either as deoxidizers or to confer specific material characteristics.
Like most black steels, this steel lacks a zinc coating, leaving the surface raw, exposed, and unprotected against corrosion in the presence of moisture or reactive chemicals. With no protective layer, it has a lower cost and is suitable for applications that are not subjected to corrosive elements. The very nature of the composition and manufacturing process of black steel gives it a wide range of applications, though it generally is not considered for highly corrosion-resistant environments.
Common Applications of Black Steel Pipe
- Gas Transportation: It is typically used for transporting gas and water under low-pressure conditions, such as within domestic and commercial plumbing systems.
- Construction Industry: Because of its strength and durability, it is widely used for structural purposes, such as scaffolding and fence frames, among others.
- Fire Sprinkler Systems: It is used in fire sprinkler systems because of its heat resistance in high-temperature environments.
Understanding Rust and Corrosion

What Causes Rust in Black Steel Pipe?
Rusting in black steel pipe occurs when the oxidation process takes place in the atmosphere. During this process, the iron content in steel can combine with oxygen in the presence of water or moisture. It creates iron oxide, or rust. Since black steel pipe is the raw steel without any protective galvanized coating, it can easily be affected by the environment, further accelerating the rate of corrosion.
Rusting in black steel pipe can occur due to many factors, such as prolonged exposure to high humidity, standing water, or harsh weather conditions. Studies have shown that steel can develop visible rusting within hours of being exposed to continuous moisture, depending on the environmental conditions. Contamination from salts or chemicals, as in marine or industrial environments, can also increase the corrosion rate by destroying surface layers of the metal, which otherwise resist oxidation.
Corrosion could occur due to MIC, where particular species of bacteria live in a humid or oxygen-deprived environment and produce various corrosive substances that weaken steel. It is equally essential to prevent rusting on black steel pipes by applying protective coatings, ensuring proper drainage, and limiting exposure to harsh environments. Regular inspection and maintenance help detect the early stages of corrosion before it starts to cause significant damage.
Differences Between Black Steel and Galvanized Steel
The Corrosion Process Explained
Corrosion is an electrochemical process by which metals like steel undergo a chemical reaction with the environment, leading to deterioration over time. Generally, three major elements are necessary for corrosion to occur: an anode, a cathode, and an electrolyte. The anode is the portion of the metal that gets oxidized as it gives up its electrons to form metal ions. The cathode is the part of the metal where reduction reactions occur, opposite to the anode, and it uses oxygen and water. The electrolyte, such as water containing dissolved salts, promotes electron transfer between the anode and the cathode.
Hazards such as humidity, oxygen concentration, pH value, salts, and other corrosive agents bring about corrosion at a high rate. For example, during highly humid instances or in coastal areas with high salt levels, the corrosion of uncoated metals is accelerated. Data also show that in the absence of even minimum protection, severe losses in material mass could occur. Untreated steel can lose up to 80 microns in thickness yearly under very aggressive circumstances.
The corrosion process can be stopped through an assortment of treatments, such as galvanization, which involves exposing steel to a zinc coating that acts as a sacrificial layer. Other corrosion treatments include employing inhibitors, protective paint coatings, and selecting suitable materials based on the environment. Understanding the corrosion processes in depth is crucial while designing systems and linking structures to assure long-term endurance and reliability.
Factors Contributing to Rusting of Black Steel Pipe

Environmental Factors
The rusting of black steel pipes heavily depends on environmental factors that help accelerate the electrochemical process of corrosion. The moisture present in the air, especially in humid climates, dramatically increases the rate of oxidation as water acts as an electrolyte, aiding in the transfer of electrons. Similarly, ground salt, whether from marine sources or de-icing salts in cold conditions, accelerates rusting because chloride ions can attack the protective film on the steel surface.
Temperature fluctuations trigger corrosion factors, as condensation can form on the pipe surface when warm air comes into contact with cooler metal. Such conditions are conducive to moisture either being present for a while or causing rust. Furthermore, polluted environments, especially those with a high concentration of sulfur dioxide or carbon dioxide, increase acidity when these gases dissolve into moisture, further accelerating the deterioration of black steel pipes. Understanding these factors is vital for implementing preemptive measures and selecting materials suited for particular environmental challenges. Appropriate assessment of atmospheric and operational conditions can synergistically further enhance the life of steel infrastructure.
Moisture and Chemical Exposure
There may be threats to the black steel pipes, especially if the humidity is too high or if different corrosive materials are around. Once moisture comes into contact with steel, it reacts with oxygen to form rust. This occurs because the corrosion process becomes more aggressive with the presence of corrosive agents in the atmosphere, such as chloride or sulfate, which further accelerate the deterioration of the surface.
Recent industrial analyses show accelerated corrosion of carbon steel in environments with chloride concentration levels exceeding 60 mg/m³, such as in the proximity of coastal areas. Similarly, the presence of sulfur emissions in industrial zones can speed up pitting and localized corrosion of steel surfaces. Also, such studies show that long-term exposure to moisture and chemicals within wastewater treatment plants or chemical plants can produce either uniform or localized wall thinning in pipes, thus hampering structural integrity.
To circumvent hazards, protective coatings like fusion-bonded epoxy or galvanized zinc are actively utilized to treat metal surfaces susceptible to harsh environments. The use of corrosion inhibitors, along with regular inspections, may be a better solution against moisture and chemical exposures. Understanding these factors and applying suitable countermeasures holds the key to protecting black steel pipe systems for an extended period and ensuring safety.
Quality of the Steel Used
The quality of steel used in making black steel pipe systems invariably determines its function and strength in various applications. In high-quality steel, such as that used in gas fittings, multiple tests are run to verify chemical composition, mechanical properties, and the correctness of processes to guarantee durability and safety. For example, the carbon content in steel determines its strength and ductility. On the contrary, low-carbon steel is commonly used in black pipe manufacture because it balances strength with machinability for structural purposes.
ASTM standards also provide stringent criteria for black steel pipes regarding dimensions, tensile strength, and impact resistance. Good manufacturing practices confer high quality, as seamless pipes can sustain higher pressure as opposed to welded pipes. On the other hand, from a metallurgical point of view, alloying additions like manganese and silicon impart favorable characteristics to steel, such as resistance to deformity and damage under stress.
Modern technologies ensure steel of the best qualities by carefully controlling impurities during production and thereby limiting the number of inclusions that could hamper performance. Consequently, choosing high-quality steel certified by suitable standards is a prerequisite for reliable and long-lasting pipe systems.
Preventive Measures Against Rusting

Using Protective Coatings
Protective coatings can form a very effective defense against rust and corrosion in steel pipes. Thus, surfaces that are coated would last longer with fewer maintenance incidents, which is desirable and raises the price. Such coatings prevent the penetration of corrosion agents, which include moisture, oxygen, and salts, into the pipe surface. Some familiar types of protective coatings are epoxy, polyurethane, and zinc-rich primers, each of them tailored to suit specific environmental or operational conditions.
Types of Protective Coatings:
- Epoxy Coatings: These are widely used in industrial applications because of their excellent adhesion, chemical and abrasion resistance, and suitability for corrosive environments, both above ground and submerged.
- Polyurethane Coatings: Polyurethane coatings can compete with the best UV inhibition coatings. It is specially developed for outdoor applications, where it is exposed to intense sunlight, and is particularly suited for use with natural gas fittings.
- Zinc-Rich Coatings: Zinc-rich coatings, such as galvanized layers, provide cathodic protection by sacrificing zinc in place of the underlying steel through galvanic corrosion. This is vital to curtailing the rust build-up in black pipe systems.
In general, paints are tested for performance by salt spray tests and cyclic corrosion testing. For instance, with appropriate application, an epoxy can endure thousands of hours of salt spray, corresponding to years of performance in adverse field conditions. Furthermore, advances in nanotechnology and green formulations will continue to grow the global market for protective coatings. Protective coatings, designed to increase toughness and meet stringent environmental regulations, are essential for preventing corrosion in water heater applications today.
Regular Maintenance Tips
Essential Maintenance Practices:
- Routine Inspections: Carry out regular inspections to look for damage in the coating, like cracks, peeling, or discoloration. If these are not taken care of, the protective layer may no longer protect adequately, and the underlying material can start deteriorating as well.
- Periodic Cleaning: It is imperative to clean the coated surface regularly because dirt, salts, and other pollutants may accelerate the rate of deterioration, especially when black pipes are used for gas. Use an abrasive-free cleaner, and always follow the instructions provided by the manufacturer to avoid damaging the coating.
- Timely Repairs: Whenever necessary, the coating should be reapplied or repaired in places that see high traffic or harsh wear.
Key Insight: Data shows that anticorrosion coatings possess high potential in resisting corrosion; with suitable upkeep, these coatings can extend performance by up to 50%, primarily in industrial or coastal applications. Thus, under the philosophy of maintenance-first, an organization can reduce heavy, long-term maintenance costs and thereby enhance the asset’s structural integrity.
Choosing the Right Pipe for Your Needs
In selecting a suitable pipe, one should always consider the end-use application. Essential considerations are pipe material, pressure ratings, temperature ratings, environmental conditions, etc. For high-temperature or high-pressure applications, metal pipes are preferred, owing to their strength and durability; stainless steel or carbon steel is generally the choice. When chemical resistance and a lighter pipe are sufficient, plastic pipes such as PVC or CPVC may be chosen. Furthermore, your pipe must meet the standards specified by the respective industry to ensure safety and performance. Choose the option that will fit best after a careful study of your system needs.
Comparisons with Alternative Materials

Galvanized Steel vs Black Steel
Benefits of Using Black Steel for Gas Pipe Applications
Black steel pipes are considered a preferred solution in gas pipeline systems owing to their outstanding physical, chemical, and functional properties. One of the key features is that black steel is robust and durable-it thus guarantees safety and reliability in the transmission of gases under high pressure. It does not require a coating in an indoor situation, which simplifies manufacturing processes and reduces costs.
The absence of zinc also means that black steel does not undergo flaking when exposed to high temperatures, which is a crucial attribute for fire sprinkler systems and any other sort of high-temperature gas application. Black steel is cost-effective because it undergoes a more straightforward manufacturing process and has been in the market for decades, proving itself especially in applications requiring strength and conductivity.
Statistical data indicate that uncoated black steel pipes, when used in suitable conditions, provide efficient service for approximately 20 to 25 years under standard maintenance regimes. Additionally, the material’s black color offers the advantage of easy recognition of pipelines during inspection and identifying systems. Such characteristics make black steel a good and practical choice for gas delivery and allied works in industrial and residential frameworks.
Cost Implications of Different Pipe Types
When we start to look at the prices and costs associated with different types of pipelines, an assortment of aspects should be taken into consideration, such as the durability of the material, the ease or complexity of installation, and the nature of maintenance. Black steel pipes have often been a cheap choice for carrying gas due to their low initial cost, minimal fabrication requirements, and the long life they offer when used under suitable conditions. Black steel pipes are priced at an average of $3 to $10 per linear foot, depending on diameter and supplier.
Comparative Pricing Overview:
Black Steel Pipes:
$3 to $10 per linear foot. This method is, however, relatively cost-efficient for gas delivery, with cheap initial costs for material supply and easy fabrication.
Galvanized Steel Pipes:
$5 to $15 per linear foot. The extra expense pays for the higher corrosion resistance conferred by the process of galvanization. But such increased resistance itself can be the basis for paying more upfront in areas where moisture content is high or where external corrosion can be a risk.
Copper Pipes:
$2-$6 per linear foot for smaller sizes and beyond $10 for larger diameter pipes. Due to increased installation costs, copper pipes are used in potable water systems because of their longevity, bacterial resistance, and recyclability.
Polyethylene (PEX) Pipes:
$1 to $2 per linear foot. Indeed, it is a more affordable and versatile alternative for residential plumbing and heating. PEX is lightweight, flexible, and relatively easy to install, which brings down the labor costs. However, long-term performance in extreme heat or outdoor conditions may be a limiting factor, especially with industrial applications.
Considering the cost of materials and labor, along with other factors, the requirements and environmental conditions specific to the project will generally determine which type of pipe is most economical and practical to use.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: Does black steel pipe rust?
A: Indeed, black steel pipe can rust. Unlike galvanized pipes, which have a zinc coating for protection, black steel pipes are just bare metal, and rust will occur when exposed to moisture and air. This issue can be minimized by proper care and the use of protective coatings.
Q: What are the applications of black steel pipe?
A: Generally, black steel pipe is used for all applications requiring strength, such as gas lines for natural gas and propane, fire protection, and water supply. It is strong enough for high-pressure applications.
Q: How does galvanized steel compare with black steel in relation to rust resistance?
A: As far as rust is concerned, galvanized steel is coated with zinc, hence being more corrosion-resistant than black steel. Black steel, without protection, is more prone to rusting, especially on humid days or when exposed to corrosive chemicals.
Q: Is rust prevention feasible on black iron pipes?
A: Yes, you can prevent rust on black iron pipes by painting the pipes or subjecting them to some kind of inhibitor. Regular inspection and maintenance are additional methods to help reduce rust formation and prolong the life of the pipes.
Q: Are black iron pipes cheaper than galvanized pipes?
A: Black iron-type pipes, being generally less expensive than galvanized pipes, are cheaper in use in areas prone to rust and corrosion, unlike galvanized pipes.
Q: What is pipe corrosion, and how does it affect black steel pipes?
A: Pipe corrosion refers to the deterioration of metal through chemical reactions with its environment. In black steel pipes, corrosion could cause leaks and loss of strength; if left untreated, it could lead to the complete breakdown of the pipe.
Q: How does one inspect black steel pipes for rust?
A: To examine black steel pipe for rust, inspect the surface visually for signs of corrosion, such as discoloration or flaking. Use a wire brush to remove loose rust and feel for any weak spots. Regular inspections permit the detection of problems before they worsen.
Q: What kind of fittings are used with black steel pipe?
A: Generally, fittings used with black steel pipe include threaded elbows, tees, and couplings. Such fittings are designed to join black steel pipes securely to offer a tight seal against leakage, whether from gas or water.
Q: What are some methods to improve the corrosion resistance of black steel pipe?
A: To enhance the corrosion resistance of black steel pipe, one should look into applying a protective coating, corrosion inhibitor, and proper drainage to avoid moisture accumulation. Also, one could use seamless pipes, which exhibit fewer locations where corrosion might begin.
Key Takeaways
- Black steel pipe rusts due to the absence of a protective coating, but it is relatively inexpensive and therefore apt for appropriate applications.
- Environmental conditions, as moisture, salt, varying temperatures, and chemical atmospheres, expedite corrosion.
- A layer of protective coating (epoxy, polyurethane, zinc-rich primers), along with maintenance, can double the operative life of the pipes up to 50%.
- Usually, black steel pipes fulfill the needs for about 20-25 years, whereas the galvanized ones last 40-50 years since a zinc coat protects them.
- If there are pipes to be selected, they must suit the requirements of the project, the environmental conditions, and the budget.
Reference Sources
- The Underground Corrosion of Selected Type 300 Stainless Steels: Corrosion was examined for a period of 33.5 years using ASTM standards and advanced analytics.
- Common Pipe Alloy Can Form Cancer-Causing Chemical in Drinking Water: This article discusses how chromium is added to iron to gain corrosion resistance.
- Pipe (fluid conveyance)
- Black Steel Pipe Supplier In China




